| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- property
- xss game 풀이
- document
- blind sql injection
- 조건문
- window
- 사칙연산
- 백준 알고리즘
- 포인터
- github
- object
- xss game
- 메소드
- Pwndbg
- jQuery
- suninatas 풀이
- element 조회
- 배열
- python
- 백준 파이썬
- IF문
- 함수
- 자바스크립트
- 객체
- 파이썬
- 김성엽 대표님
- sql injection
- htmlspecialchars
- lord of sql injection
- burp suite
- Today
- Total
power-girl0-0
문서의 기하학적 특성 본문
생활코딩 웹브라우저 javascript를 참고하여 공부하였습니다.
스스로 공부한 것을 정리하고 복습하기 위한 목적으로 작성하였습니다.
( 출처 : https://opentutorials.org/course/743inf.run/pBzy)
요소의 크기와 위치
아래 예제를 통해서 element의 크기를 알아내는 방법을 살펴보자. (실행 결과)
<style>
body{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
#target{
width:100px;
height:100px;
border:50px solid #1065e6;
padding:50px;
margin:50px;
}
</style>
<div id="target">
Coding
</div>
<script>
var t = document.getElementById('target');
console.log(t.getBoundingClientRect());
</script>위 소스코드를 실행한 결과 아래와 같이 출력되며, 크기에 대한 것은 보기 쉽게 직접 그린 것이다.
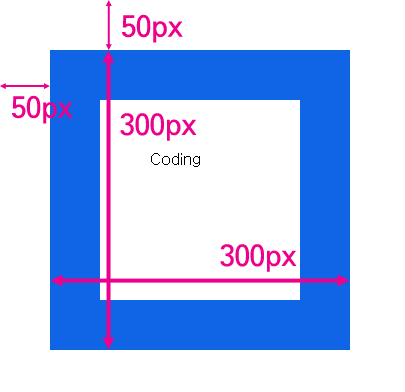
즉 element의 테두리와 body 태그 사이의 거리가 50px이고, 테두리를 포함한 element의 크기는 300px이다.
해당 값을 알아내고 싶을 때, 사용하는 API가 getBoundingClientRect이다.
이 api를 콘솔에서 실행하면, 아래와 같이 출력된다.

getBoundingClientRect의 width, height값을 윈도우 익스플로러(IE) 에서는 제공하지 않는다.
만약 element가 중첩되어 있다면 어떻게 될까?(실행 결과)
즉, div안에 div를 중첩시켰을 때 어떻게 출력될까에 대해서 알아보자.
<style>
body{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
div{
border:50px solid #1065e6;
padding:50px;
margin:50px;
}
#target{
width:100px;
height:100px;
}
</style>
<div>
<div id="target">
Coding
</div>
</div>
<script>
var t = document.getElementById('target');
console.log(t.getBoundingClientRect());
console.log(t.offsetParent);
</script>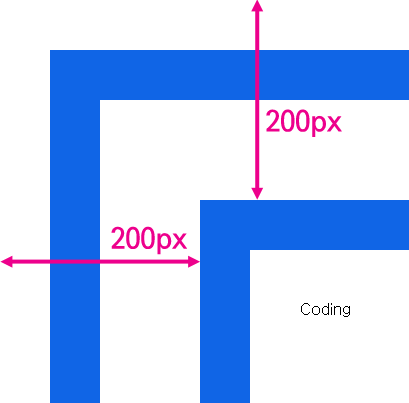
위와 같이 엘리먼트를 중첩했을 때 coding과 문서와의 거리는 200px이다. getBoundingClientRect를 호출해보자.
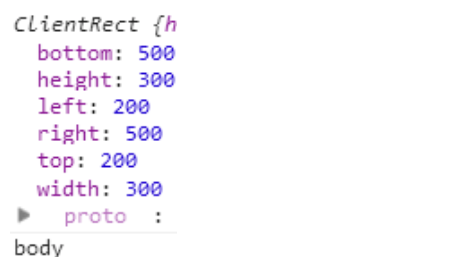
즉 엘리먼트의 위치를 의미하는 top, right의 값을 통해서 기준이 그 부모가 아니라 body라는 것을 알 수 있다.
이를 명시적으로 확인할 수 있는 방법은 offsetParent 속성을 호출하는 것이다.
즉, 측정의 기준이 되는 element가 누구였는가를 알고 싶을 때 사용한다.
하지만 body가 항상 기준점이 되지 않는다는 것을 암시적으로 알 수 있다.
만약 부모 중 CSS position의 값이 static인 td, th, table 엘리먼트가 있다면 이 엘리먼트가 offsetParent가 되는 예외가 있기 때문이다.
오래된 브라우저에서는 getBoundingClientRect를 지원하지 않을 수 있기 때문에 이런 경우 offsetLeft와 offsetTop 프로퍼티를 사용한다.
테두리를 제외한 element의 크기를 알고 싶다면 ClientWidth, ClientHeight를 사용한다. (실행 결과)
<script>
var t = document.getElementById('target');
console.log('clientWidth:', t.clientWidth, 'clientHeight:', t.clientHeight);
</script>Viewport
요소의 위치를 생각할 때는 문서가 브라우저의 크기보다 큰 경우는 스크롤이 만들어지는데 스크롤에 따라서 위치의 값이 달라지기 때문에 복잡하다.
이를 이해하기 위해서는 우선 viewport에 대해 알아보자.
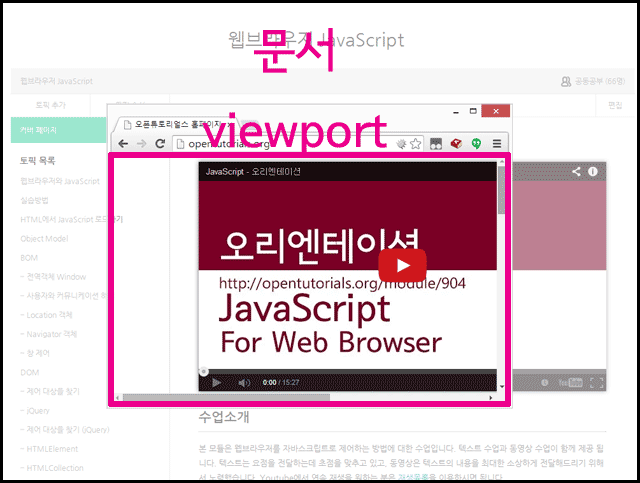
viewport의 좌표
위의 그림처럼 viewport는 문서의 내용 중 사용자에게 보여주는 영역을 의미한다.
이에 따라서 문서의 좌표가 있고 viewport의 좌표가 있다.
우리가 위에서 살펴본 getBoundingClientRect는 viewport의 좌표를 사용한다.
아래 예제는 1초에 한번씩 getBoundingClientRect의 top 속성과 window.pageYOffset의 값이 출력된다. (실행 결과)
<style>
body{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
div{
border:50px solid #1065e6;
padding:50px;
margin:50px;
}
#target{
width:100px;
height:2000px;
}
</style>
<div>
<div id="target">
Coding
</div>
</div>
<script>
var t = document.getElementById('target');
setInterval(function(){
console.log('getBoundingClientRect : ', t.getBoundingClientRect().top, 'pageYOffset:', window.pageYOffset);
}, 1000)
</script>
이를 통해서 알 수 있는 것은 getBoundingClientRect의 값이 스크롤에 따라서 달라지는 뷰포트의 좌표를 사용하고 있다는 것이다.
또한 스크롤의 정도를 알고 싶을 때는, pageYOffset을 사용하면 된다.
오래된 브라우저에서는 pageYOffset 대신 scrollTop 속성을 사용해야 한다.
문서의 좌표
뷰포트의 좌표에 스크롤된 정도를 더해서 알 수 있다.
즉, 아래 코드와 같이 getBoundingClientRect의 값과 pageYOffsen값을 더하면 문서의 좌표를 알 수 있다.
(실행 결과)
setInterval(function(){
console.log('getBoundingClientRect : ', t.getBoundingClientRect().top, 'pageYOffset:', window.pageYOffset, 'document y:', t.getBoundingClientRect().top+window.pageYOffset);
}, 1000)스크롤
문서의 스크롤 값을 변경하는 것은 scrollLeft와 scrollTop 프로퍼티를 이용하면 된다. (실행 결과)
<style>
body{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
div{
border:50px solid #1065e6;
padding:50px;
margin:50px;
}
#target{
width:100px;
height:2000px;
}
</style>
<input type="button" id="scrollBtn" value="scroll(0, 1000)" />
<script>
document.getElementById('scrollBtn').addEventListener('click', function(){
window.scrollTo(0, 1000);
})
</script>
<div>
<div id="target">
Coding
</div>
</div>즉, 자바스크립트를 통해서 스크롤을 제어할 수 있다는 것을 알 수 있다.
스크린의 크기
스크린의 크기는 모니터의 크기와 브라우저 뷰포트의 크기가 있다. (실행 결과)
<script>
console.log('window.innerWidth:', window.innerWidth, 'window.innerHeight:', window.innerHeight);
console.log('screen.width:', screen.width, 'screen.height:', screen.height);
</script>
window.inner*은 뷰포트의 크기를 나타내고, screen.*은 웹 브라우저를 사용하는 사용자의 모니터 크기를 나타낸다.
참고
'언어 > Javascript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| inline ( 인라인 방식 ) (0) | 2021.02.10 |
|---|---|
| 이벤트 (0) | 2021.02.10 |
| Text 객체 (0) | 2021.02.10 |
| Document 객체 (0) | 2021.02.10 |
| [ Node ] 문자열로 노드 제어 (0) | 2021.02.10 |




